Summary
While there isn’t anything necessarily inherently insecure about AD CS (except for ESC8 as detailed below), it is surprisingly easy to misconfigure its various elements, resulting in ways for unelevated users to escalate in the domain.
Personnally I have mainly encountered ESC1 and ESC4 abuses. I will try to update this articles as times passes or get time for Lab checks and evidence searching.
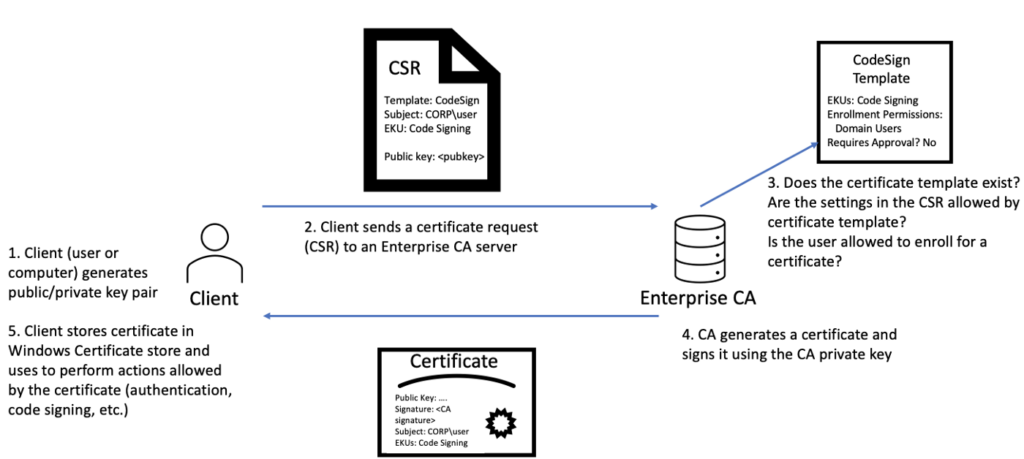
Attacks
| name of Attack | Description |
|---|---|
| ESC1 | Domain escalation via No Issuance Requirements + Enrollable Client Authentication/Smart Card Logon OID templates + CT_FLAG_ENROLLEE_SUPPLIES_SUBJECT |
| ESC2 | Domain escalation via No Issuance Requirements + Enrollable Any Purpose EKU or no EKU |
| ESC3 | Domain escalation via No Issuance Requirements + Certificate Request Agent EKU + no enrollment agent restrictions |
| ESC4 | Domain escalation via misconfigured certificate template access control |
| ESC5 | Domain escalation via vulnerable PKI AD Object Access Control |
| ESC6 | Domain escalation via the EDITF_ATTRIBUTESUBJECTALTNAME2 setting on CAs + No Manager Approval + Enrollable Client Authentication/Smart Card Logon OID templates 6 |
| ESC7 | Vulnerable Certificate Authority Access Control ESC8 NTLM Relay to AD CS HTTP Endpoints |
Resources
Links to resources of interest:
- SpecterOps Certified_Pre_Owned page which includes the list of conditions to be met for each attack
- SpecterOps Certified_Pre_Owned full paper
- PowerShell toolkit for auditing ADCS
List of tools used (non exaustive)
- Certify (C#)
- InvokeCertify (Powershell)
- CertiPy (Python)
- Masky
- CME + Masky Module
- ADCSPwn
Tracking Exploitation
Check in the PKI the certs delivered (you can find the Requester Name and the Certificate Template Name and it’s SN)
If no access to the ADCS interface to see the certs, you can copy the EDB file from C:\Windows\System32\CertLog\CA_NAME.edb
And use ESEDatabaseView from NirSoft to read it.
In the RequestAttributes you can easily find the compromises of SAN

ESC1 attack evidences
For ESC1 (most common abuse, as tools implement from user -> DA elevation)
Check the certificate SAN field
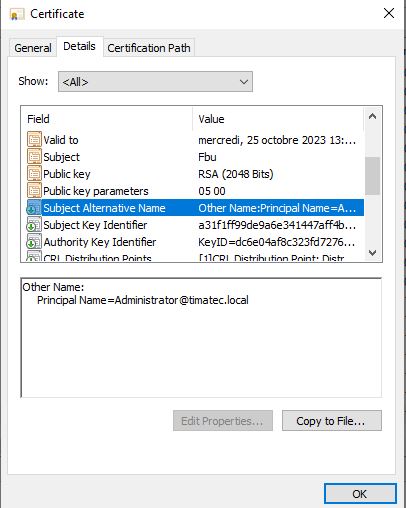
Then you can check 4624 Security Events with schannel as type.
And also 4768 Security Events (get Kerberos ticket from Cert Authentication)
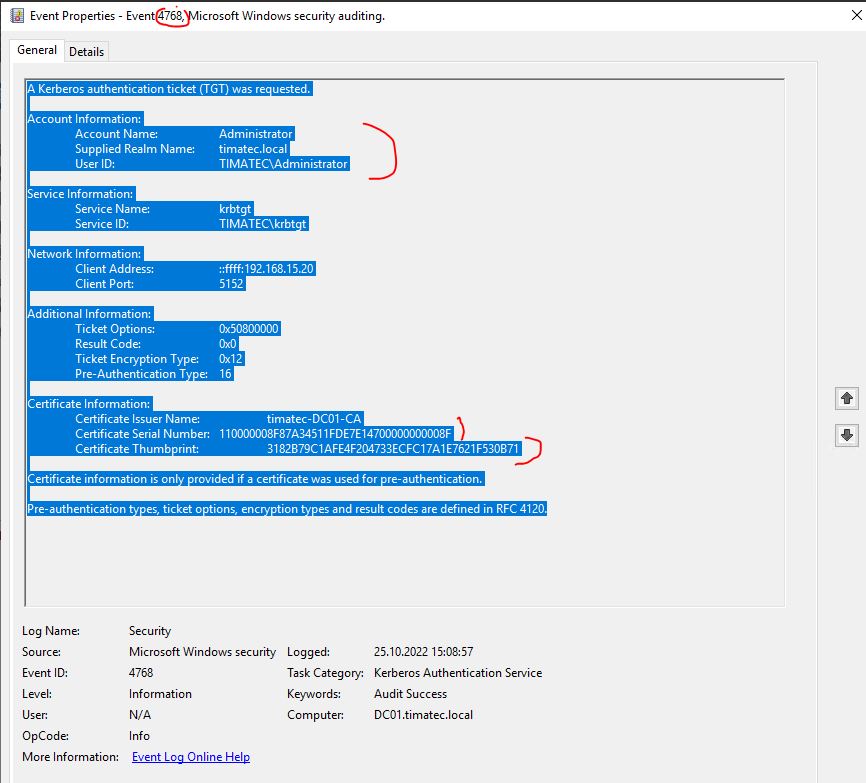
Note : With PKINIT one can retrieve the NTLM Hash from the Cert Authentication
Containment Options
Detail how the vulnerability can be temporariliy mitigated during IR
Eradication
Disable the vulnerable templates
Clean-up methods
Revoke all compromised/(all if uncertain) certs
0
Recent Comments